Experiential Learning - Let the experience do the teaching
Experiential Learning - Let the experience do the teaching
Editorial Team
theteacher.in
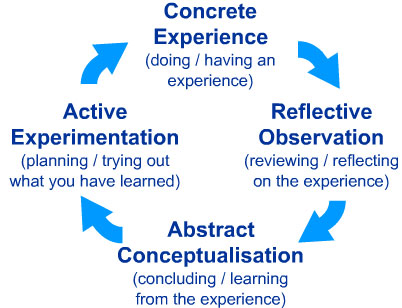 In 1984, David A. Kolb published a groundbreaking book titled ‘Experiential Learning’. This book essentially exposed the principle that a person learns through discovery and experience. In addition, Kolb demonstrated that there was more than one style of learning. According to Kolb, learning styles may be seen through two continuums; going from concrete to abstract and active to reflective. Processing information and perceiving information represent the two continuums identified by Kolb. According to him, a learner will evolve on these continuums because of his or her apprehension and preferences in processing or perceiving information. He suggested that it was preferable for a student to learn through this cycle, allowing him or her to experiment with four learning styles in order to have a better understanding of a subject.
In 1984, David A. Kolb published a groundbreaking book titled ‘Experiential Learning’. This book essentially exposed the principle that a person learns through discovery and experience. In addition, Kolb demonstrated that there was more than one style of learning. According to Kolb, learning styles may be seen through two continuums; going from concrete to abstract and active to reflective. Processing information and perceiving information represent the two continuums identified by Kolb. According to him, a learner will evolve on these continuums because of his or her apprehension and preferences in processing or perceiving information. He suggested that it was preferable for a student to learn through this cycle, allowing him or her to experiment with four learning styles in order to have a better understanding of a subject.Certain technologies or educational activities would be more appropriate to a specific learning style. The following table provides definitions for each of the learning styles.
| Style | Definition | Educational implications |
|---|---|---|
| Innovator |
|
|
| Analytical |
|
|
| Practical |
|
|
| Dynamic |
|
|





















