Reciprocal Teaching in the Classroom
Reciprocal Teaching in the Classroom
Most often, in a traditional classroom setting, teachers guide discussions without inversing the roles of teachers and students, which makes it difficult for the latter to learn about guiding and handling discussion in groups. However, with the introduction of reciprocal teaching, the method of learning has become an interesting one.
What is Reciprocal Teaching?
 Reciprocal Teaching refers to an instructional activity in which students become the teachers in small group reading sessions. Teachers model the students and help them learn to guide group discussions using four strategies which are- summarising, questioning, clarifying and predicting. This form of teaching helps make students the active participants in classrooms. It also helps students transcend from guided to independent readers and reinforces strategies for comprehending the meaning of the text.
Reciprocal Teaching refers to an instructional activity in which students become the teachers in small group reading sessions. Teachers model the students and help them learn to guide group discussions using four strategies which are- summarising, questioning, clarifying and predicting. This form of teaching helps make students the active participants in classrooms. It also helps students transcend from guided to independent readers and reinforces strategies for comprehending the meaning of the text.Reciprocal Teaching technique was developed in the 1980s by two university professors- Annemarie Sullivan Palinscar and Ann. L. Brown. Using reciprocal teaching, improvements have been noted in student reading comprehension in as little as three months and maintained up to a year.
In the reciprocal teaching method, the teacher models comprehension strategies- summarising, questioning, predicting and clarifying through guided group discussions. Once the students are comfortable with the process and the strategies, they take turns leading similar discussions in small groups.
The four-strategies
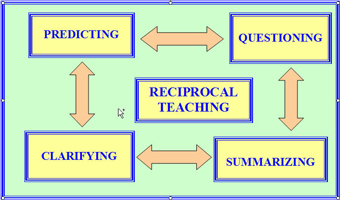 Sometimes called the ‘Fab Four’, the strategies used in reciprocal teaching work towards increasing comprehension. The four elements are as follows-
Sometimes called the ‘Fab Four’, the strategies used in reciprocal teaching work towards increasing comprehension. The four elements are as follows--
Summarising- Summarising is a very vital skill for readers of all ages. It requires the students to use a summarising strategy to pick out the main idea and key points from the text. The students then put the information together in order to concisely plan the main meaning and context of the passage in their own words.
Some of the questions that can be addressed through the following-
-
What is the most important part of the text?
-
What happened first?
-
What is it mostly about?
-
How does it end? Or how was the problem resolved?
-
Questioning- Questioning helps students develop their critical thinking skills. Enable the students to model this skill by encouraging them to dig deep and analyse.
Some of the questions that can encourage students to question the text are as follows-
-
Why do you think?
-
What do you think?
-
When did the incident happen, etc?
-
Predicting- Predicting is the skill of making an educated guess. Students can develop this skill by looking at clues in the text closely in order to determine its outcome.
Help students practice this skill by giving open-ended phrases such as I believe, because of…, etc-
-
I think the book is about ___because...
-
I predict I will learn because…
-
I think the author is trying to say…
-
 Clarifying- Clarifying involves the use of strategies to understand unfamiliar words or texts as well as self-monitoring one's progress in overall reading comprehension. Modeling clarifying techniques such as re-reading or using the glossary to understand difficult words enables the reader to get a clearer idea of the text-
Clarifying- Clarifying involves the use of strategies to understand unfamiliar words or texts as well as self-monitoring one's progress in overall reading comprehension. Modeling clarifying techniques such as re-reading or using the glossary to understand difficult words enables the reader to get a clearer idea of the text-
-
I didn’t understand the part because…
-
This is difficult because…
-
I am having trouble because…
Importance of reciprocal teaching-
-
Reciprocal teaching encourages students to think and form their own thought process during the reading activity.
-
It encourages students to be actively involved in group discussions and also helps monitor their comprehension skills as they read.
-
It teaches students to actively ask questions during reading session and also helps to make the text more comprehensible to them.
As students become comfortable in reading comprehension using this technique, ensuring that each student takes a turn in leading the discussion will help students understand, learn and lead the discussions pro-actively.























